LUPOS DIŞ TİCARET

Shipping & Logistics from China to Turkey
Importers can choose between sea freight, air freight, and rail freight, with delivery options such as port-to-port, door-to-door, and port-to-door. The right choice depends on your cargo volume, budget, and delivery timeline.
Sea Freight Shipping Options
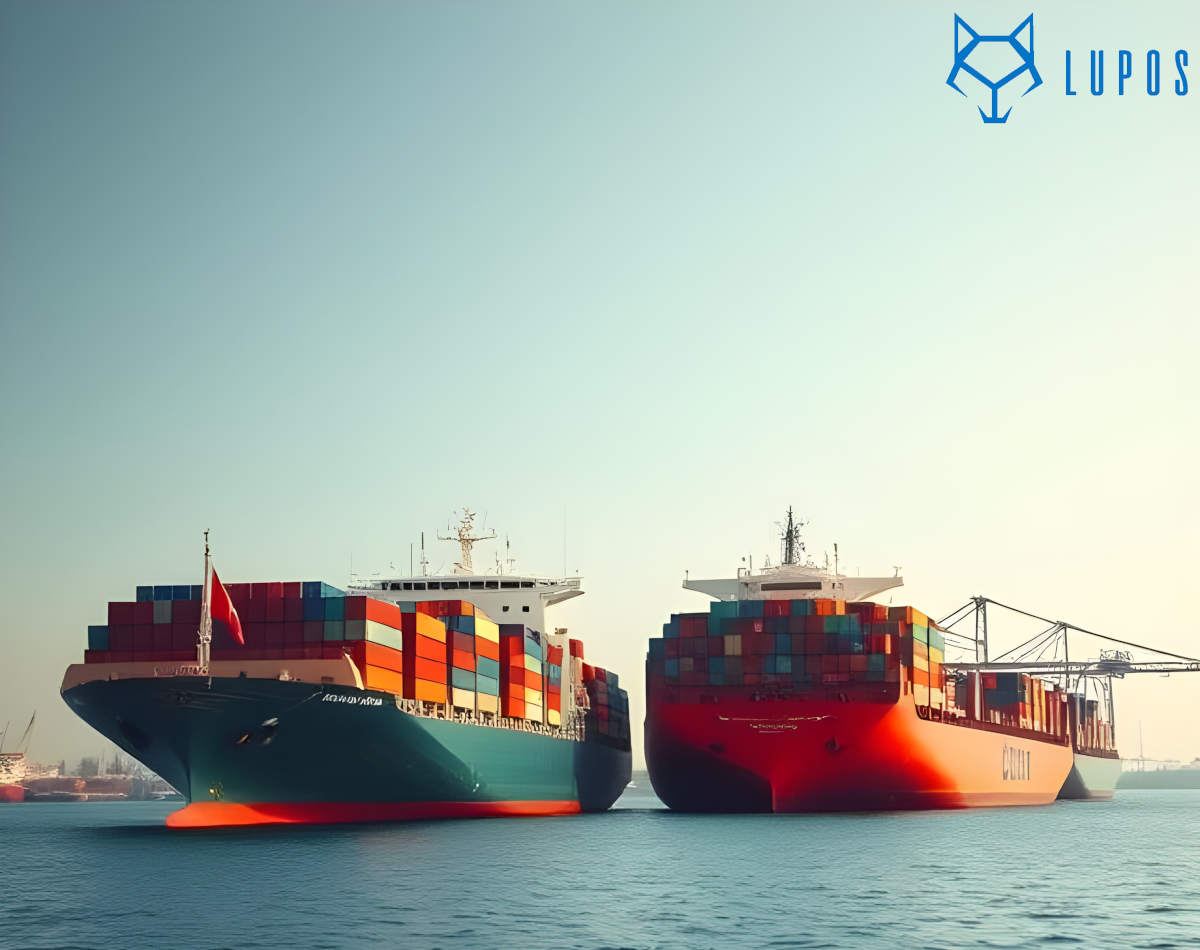
Sea freight is the most common and cost-effective solution for bulk imports. It comes in two main types:
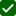
LCL (Less than Container Load)
- Multiple shippers share space in a single container.
- Ideal for smaller shipments (typically 2–13 cubic meters).
- Cost-effective but slightly slower due to multiple handling stages during consolidation and deconsolidation.
FCL (Full Container Load)
- A single shipper rents or owns the entire container.
- Recommended for larger shipments (above 13 cubic meters) or high-value goods.
- Faster, more secure, and involves less handling — the container remains sealed until delivery.
Shipping Terms Explained

Port-to-Port
- Covers only sea transport between the origin and destination ports.
- The importer is responsible for customs, inland transport, and delivery after arrival.
- Most cost-effective but requires strong logistics coordination.
Door-to-Door
- The freight forwarder handles pickup, transport, customs, and final delivery.
- Simplifies the process for importers but is generally more expensive.
Port-to-Door
- A hybrid option: freight covers from the origin port to the buyer’s address.
- Reduces complexity for the importer, typically priced between port-to-port and door-to-door.
Each shipping method varies in cost, responsibility, and convenience — if you’re unsure which option fits your business, contact Lupos Dış Ticaret for tailored import planning and logistics support.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) shipping is especially popular for first-time importers. Under DDP, the seller or freight forwarder manages the entire delivery process — including freight, customs clearance, taxes, and final delivery.
This method is ideal for buyers without a Turkish tax ID or import experience.

Customs and Import Regulations in Turkey
Turkey allows the import of most goods, except for restricted or prohibited items related to health, environment, or national security.
Key points to consider:
- Some products require import permits managed by the Turkish Ministry of Trade
- Customs duties, Special Consumption Tax (ÖTV), and Value-Added Tax (VAT) (usually 20%) apply depending on product type.
- Required documents typically include a Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Certificate of Origin, and other product-specific certificates.
- For more details, review the official Turkish Customs import regime.
Key Documents for Importing to Turkey
Import documentation must be accurate and consistent. Commonly required paperwork includes:
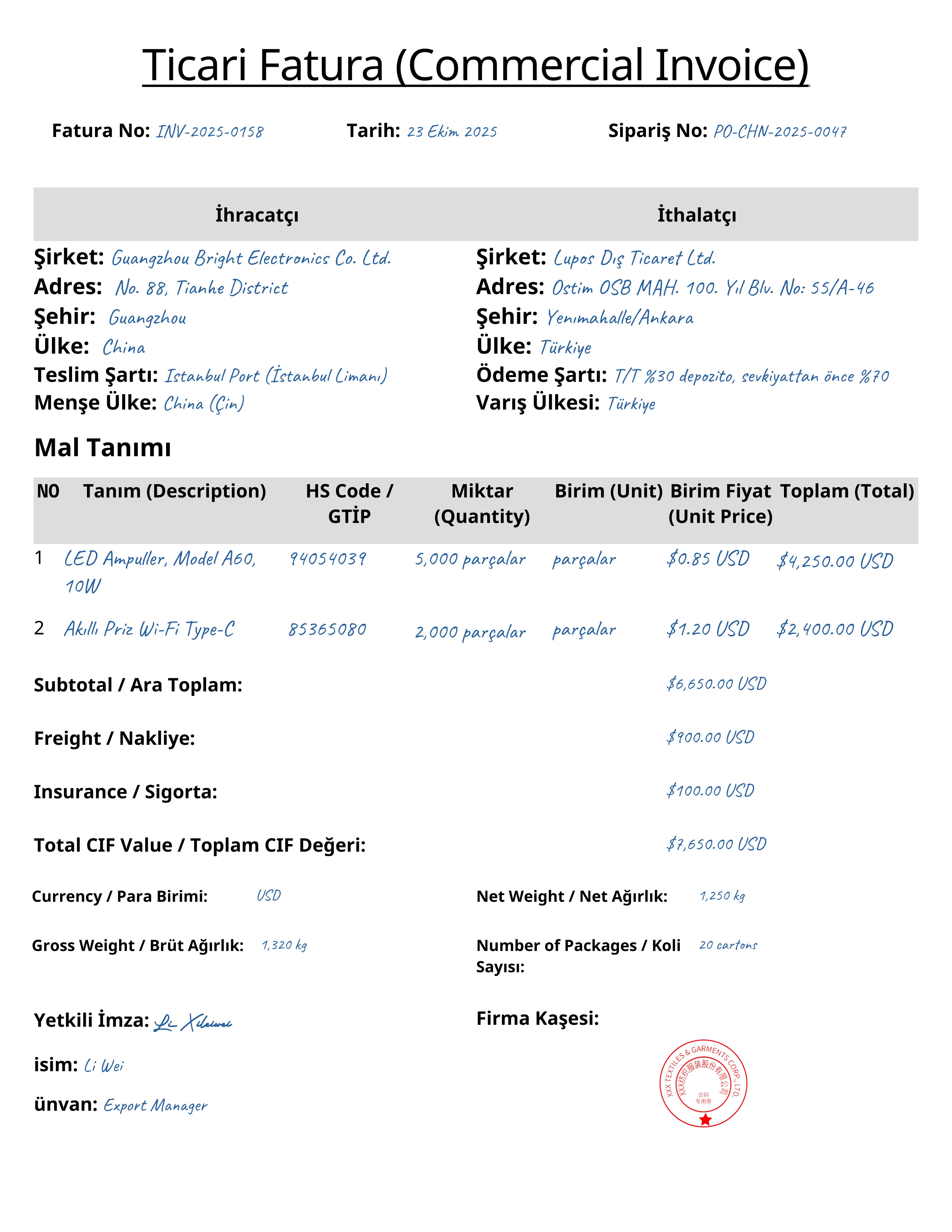
- Commercial Invoice
- Must be issued in triplicate.
- Includes product description, HS code, unit price, origin, and delivery method.
- Official U.S. trade guide on Turkish import documentation
- Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
- Proof of shipment contract and goods receipt.
- Details must match other shipping documents.
- Customs clearance guide in Turkey
- Packing List
- Details packaging, weight, and item quantities for inspection.
- Certificate of Origin
- Confirms where the goods were produced.
- Must be certified by a chamber of commerce or Turkish consulate.
- Additional Certificates (if applicable)
- For food, agriculture, or regulated goods: health, phytosanitary, veterinary, or CE conformity certificates.
- Summary Declaration
- Filed before goods enter Turkish territory, usually by the importer or carrier.
Download Sample Import Documents (PDF & DOCX)
Importing into Turkey requires accurate documentation. Below you can download sample templates of the most commonly used import documents.
How to Calculate Import Taxes and Duties in Turkey
Import taxes are calculated based on the CIF value (Cost + Insurance + Freight). The main steps include:
- Determine Customs Value (CIF)
- Total = Product cost + insurance + freight + packaging.
- Apply Customs Duty Rate
- Based on product classification (GTIP) and country of origin.
- Apply Special Consumption Tax (ÖTV)
- Applies to select goods (e.g., tobacco, alcohol, vehicles).
- Calculate Value Added Tax (VAT)
- Applied on the total of CIF + duty + ÖTV.
- Rates: 1%, 8%, or 20% depending on category.
- Consider Other Fees (e.g., RUSF)
- Imports on credit may be subject to a 6% Resource Utilization Support Fund.
Formulas:
Customs Duty = CIF × Duty Rate
SCT (if applicable) = (CIF + Customs Duty) × SCT Rate
VAT = (CIF + Customs Duty + SCT) × VAT Rate
Final Thoughts
Importing from China to Turkey offers great opportunities for wholesalers and retailers — but success depends on logistics planning, customs compliance, and accurate documentation.
For personalized consulting, cost estimates, or full-service import management, contact Lupos Dış Ticaret — your trusted China import partner in Turkey.